The Rhine
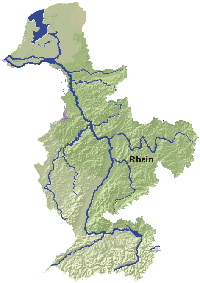
During the past centuries the Rhine has undergone considerable structural and functional changes. Its expansion to the busiest and most important European inland waterway starting 130 years ago and its use for industrial draining starting around the same time caused the river to become increasingly desolate ecologically.
Due to far-reaching measures the Rhine is again in good shape today. The vision of a river which can tolerate all the uses assigned to it in the long run has come within reach.
- The Rhine as an inland waterway is indispensable when coping with the steadily increasing transport of goods;
- it provides recreational facilities for the inhabitants of the conurbations close to the Rhine;
- the Rhine helps to discharge waste water;
- it enables the generation of electrical energy using water power;
- the Rhine is an indispensable and irreplaceable source of drinking water.
In order to cope with all these uses a sound ecological system is indispensable. In the past years further aspects have come up emphasizing the Rhine :
- The Rhine should again become a native habitat for more fishes. This not just presupposes good water quality but also the removal of obstacles at sluicegates and weirs to facilitate migration of fish.
Flood protection along the densely populated shores of the Rhine is gaining importance. The protection of human life and material values should be improved. At the same time changes in the course of the river due to construction and climatic changes will be taken into account.
| Length of the River | 1 230 kms |
| Size of catchment area | 185 000 kms² |
| Population in the catchment area | 61 million |
| Drinking water from the Rhine | Directly or indirectly from the Rhine approx. 30 million |
| population density | 324 Inhabitants/km² |
|
Countries in the catchment area |
|
| Germany | approx. 105 000 kms 2 |
| Netherlands | approx. 34 000 kms 2 |
| Switzerland | approx. 28 000 kms 2 |
| France | approx. 24 000 kms 2 |
| Luxemburg | 2 500 kms 2 |
| Austria | 2 400 kms 2 |
| Italy , Liechtenstein , Belgium | small part each |
|
Headstreams |
|
| Vorder- and Hinterrhein | Switzerland |
|
Six sections |
|
| Alpine Rhine | from confluence of headstreams near Reichenau ( Switzerland to Lake Constance ) |
| High Rhine | outlet Lower Lake to Basle |
| Upper Rhine | Basle to Bingen |
| Central Rhine | Bingen to Bonn |
| Lower Rhine | Bonn to Lobith |
| Rheindelta | Lobith to North Sea |
|
Important tributaries |
|
| Aare | Switzerland |
| Neckar | Germany |
| Main | Germany |
| Nahe | Germany |
| Lahn | Germany |
| Mosel with Saar | Germany |
| Ruhr | Germany |
| Lippe | Germany |
